Supplements: Vitamin D
Vitamin D is mainly helpful for your bone development either for the very old or young. Always consult a doctor when supplementing on top of a healthy diet. Lack of Vitamin D can cause rickets and osteomalacia. Main sources of Vitamin D are sunlight and fatty fish.
What is Vitamin D ?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin who promotes the absorption of intestinal absorption intestinal absorption of calcium, iron, magnesium,phosphate, and zinc. There are four forms of Vitamin D which are known as
- Vitamin D1 (Ergocalciferol with Lumisterol)
- Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol made from ergosterol)
- Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol made from 7-dehydrocholesterolin the skin)
- Vitamin D4 (22-dihydroergocalciferol)
- Vitamin D5 (sitocalciferol made from 7-dehydrositosterol)
The most common debated versions of Vitamin D for supplement purposes are Vitamin D2 and D3. Vitamin D2 has been first discovered in 1931 followed by D3 in 1935. You can increase the vitamin D levels in your system by
- Eating a healthy diet
- Going out into the sun
- Supplement Vitamin D as a pill
Very few foods contain Vitamin D naturally, therefore the main source of vitamin D is synthesis via the skin in the form of Vitamin D3. In this process, 7-dehydrositosterol is converted into Vitamin D3 in animals in two steps involving ultraviolet light.
For this process to work the UV light has to penetrate the skin. This is why Vitamin D deficiency is often linked to countries with less exposure to sunshine (like Ireland) or people with darker skin. UV light at a wavelength of 290 - 320 nanometers penetrates the uncovered skin. Cloud cover and shade reduce the UVB intensity by 50 - 60%. UVB does not penetrate glass, therefore staying inside at a window does not work with the production of Vitamin D3 by the skin.
While it is often claimed, regularly in combination with proposing a need for supplementing Vitamin D, that in far north latitudes and for dark-skinned individuals it is hard to obtain enough Vitamin D via exposure to sunlight, there are also studies who propose that these factors do not inhibit Vitamin D3 production in the body.
The daily recommendations for exposure to the sun for sufficient Vitamin D production vary from 5 - 30 minutes twice daily depending on the source. You will be hard pressed to find official recommendations by government bodies due to the cancer risk that correlates with too much sun exposure. As a rule of thumb for daily use: "Use no sunscreen and avoid sunburn" which can vary considerably from day to day and region. The sun is less likely to provide your daily needs at higher latitudes, in the winter, or if you're older,
An additional source of Vitamin D can and should be your diet.Conditions like milk allergies, lactose intolerance, ovo-vegetarianism and veganism can lead to a lower level of Vitamin D being taken in through your diet. In combination with little sun exposure, this can lead to Vitamin D deficiency. This has become a worldwide issue among the elderly and common in children and adults. A deficiency of Vitamin D is reached at <30nmol/l of serum 25 OHD, the best indicator for Vitamin D levels in humans to date. If you wanted to counteract these trends in your personal case through your diet good sources of Vitamin D are:
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Mackerel
- Fortified milk
- Fortified margarine
To a lesser extent
- Beef liver
- Egg yolks
- Yogurt
- Cheese
In the United States and Canada, milk and margarine are being fortified since it is known that Vitamin D has positive effects for children to avoid rickets. Rickets is a softening of the bones which lead to malformation of the legs and other bone structures if babies between 0 -.12 months develop a Vitamin D deficiency.
The third source of vitamin D is to supplement in the form of pills. These come in various forms and colours. You can see a selection of product at the website of boots or hollands & barrets.
Following tables taken from the National Institue of health will help you to stay on top of your Vitamin D intake:
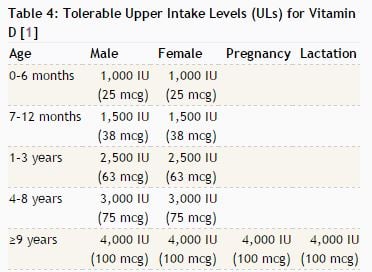
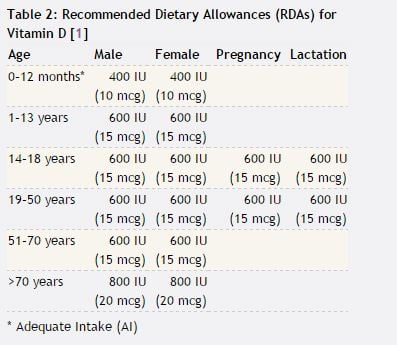
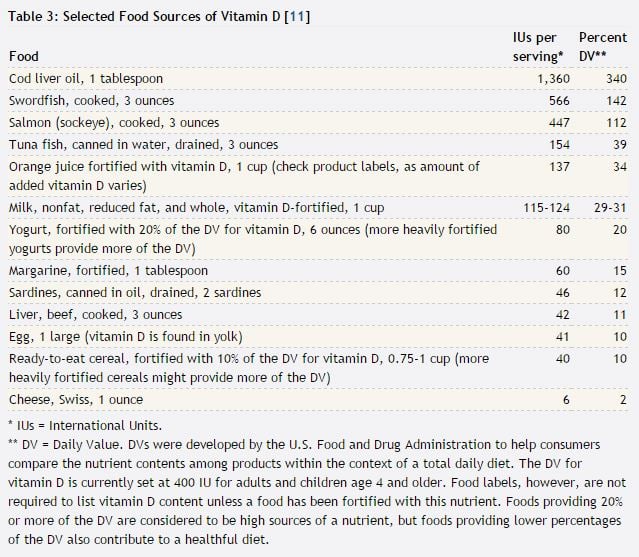
Average intake levels for males from food range from 204 to 208 UI a day, for females between 144 to 276. For older women from 51 - 70 it was 156 UI in the median and for women over seventy 180 UI Day. The women under the same report who took supplements were around 400 UI. If you want an article that can be easily read on how to manage Vitamin D intake and which foods work, as tables are not for everyone, go to this article on vitamin D intake on health.com.
What are the benefits of Vitamin D ?
Vitamin D helps to maintain adequate serum calcium and phosphate concentrations which are linked to bone stability and growth. It is also believed to prevent rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Vitamin D is also connected to the modulation of cell growth, immune function, reduction of inflammation and neuromuscular and immune functions. There are several instances where Vitamin D intake is also said to have a positive influence on cancer and other diseases, however, a big study from 2009 to 2013 concluded that it is still not possible to specify a relationship between vitamin D and health outcomes other than bone health.
What are the risks of Vitamin D ?
The biggest dangers with interventions like supplementing Vitamin D is when they are being misunderstood and people overdose. In the case of Vitamin D this would mean taking to many Vitamin D pills causing Vitamin D toxicity in the body or exposing yourself to long to UV light via natural sun or under a sunbed exposing yourself unnecessarily to a higher risk of skin cancer.
Vitamin D toxicity can lead to
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- Polyuria
- Heart Arrhythmias
- Vascular calcification
- Tissue calcification
Toxic intakes from food or sunlight for Vitamin D are unlikely. If it occurs it is usually because of taking too much Vitamin D in for of a supplement.
Conclusion
Vitamin D is a good supplement for anyone who is at risk of brittle bones because of their age, medical circumstances or diet choices. For generally healthy people with healthy diets, there seems to be slim to no added benefit of taking supplements for Vitamin D. If you get your vitamin D take care to avoid sunburn. Most recently the pollution of the oceans raises concerns around fish consumption due to plastic and copper being in their diets. I will not cover this in this article, but something to keep in mind.
Further Reading
- Colostrum
- Creatine
- Digestive Enzymes
- Electrolytes
- Fish Oil
- GABA
- Glucosamine
- Glutamine
- How much do I have to pay for supplements
- Multi-Vitamin
- Probiotics
- Protein
- Vitamin C
- What are supplements
- Which supplements are sold the most
- ZMA


